
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
The Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) allows you to compensate for a logically unique part of the AWS Cloud. In a virtual network, you can use AWS resources. You have full access and control over your VN environment, also comprising a selection of your creation of subnets, private IP address range, and also the configuring of network gateways and route tables. You can use both IPv4 and IPv6 in your Amazon VPC for easy and secure access to applications and resources.
You can customize your premise network configuration of your individual Amazon VPC. You can also use many security layers, including premises, access control database, and security groups, to help in controlling the access to Amazon EC2 instances in every subnet.
The AWS services that can be used with Amazon VPC as follows
- Amazon EC2
- Amazon Route 53
- Amazon WorkSpaces
- Amazon OpsWorks
- Amazon Redshift
- Auto Scaling
- Elastic Load Balancing
- Amazon Elasticache
- AWS Data Pipeline
- Elastic Beanstalk
- Amazon EMR
- Amazon RDS
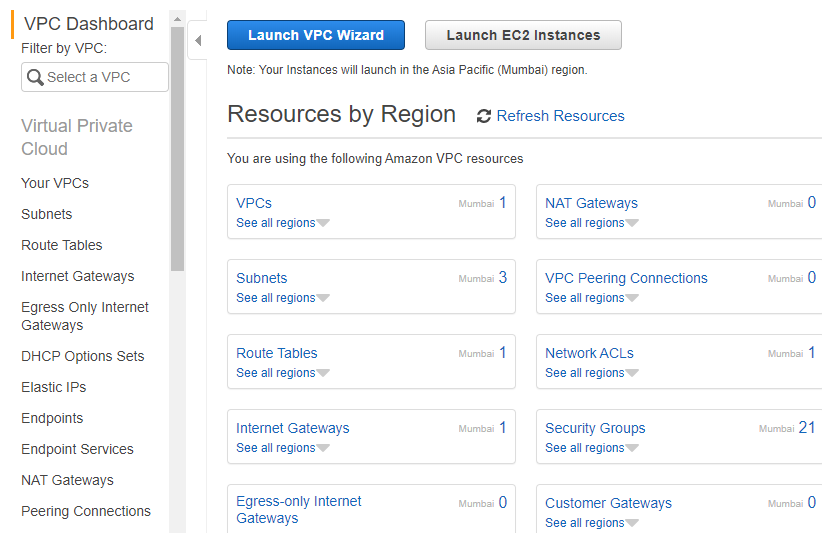
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Concept
The Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is the network building layer for Amazon EC2. The below concepts are the key factors for Amazon VPCs:
- A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a structure of a virtual network desired to your individual AWS account.
- In your private VPC, a subnet is nothing but a range of IP addresses.
- A routing table contains rule routes that are set, which is used to identify the direction of network traffic.
- An internet gateway denotes a redundant, horizontally scaled, and has a high availability of the VPC component that permits communication between the internet and occurrences in your VPC.
- An endpoint of a VPC permits you to specially create a connection in between your VPC to a supported VPC endpoint service and the AWS services empowered by the PrivateLink without the requirement of an internet gateway, Network Address Translation device, Virtual Private Network connection, or an Amazon Web Services Direct Connect interlink. Incidents in your VPC don’t need public Internet Protocol addresses to exchange information with resources in the undertaken work. Traffic among the other service and your VPC doesn’t exclude the Amazon network.
How to Use Amazon Virtual Private Cloud?
The steps to create VPC are discussed below
To create Virtual Private Cloud
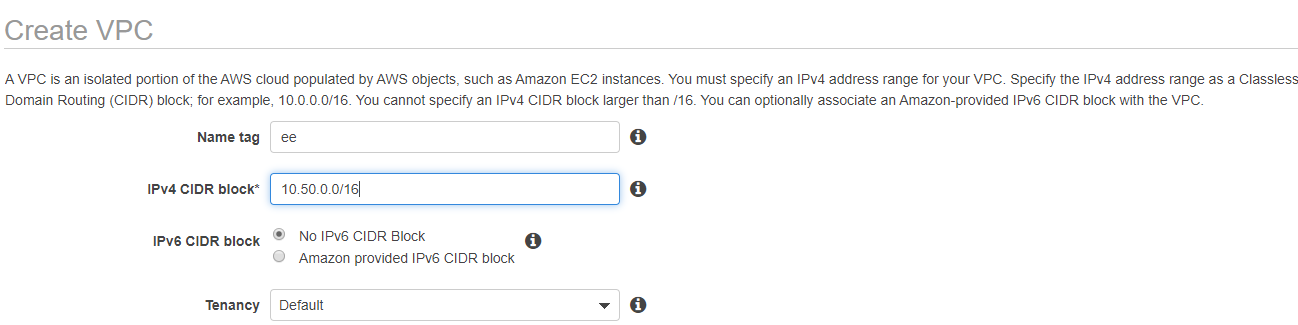
- You have to get signed in to the AWS Management Console and attempt to open the Amazon VPC console.
- You should select creating a totally new Amazon VPC option with the help of the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud wizard option from the navigation bar. You should select a similar region for other AWS services.
- Found in the navigation bar, select a VPC Dashboard, click the Start VPC Wizard button, then select VPC with a single public subnet option from the left side which is a default option to create VPC.
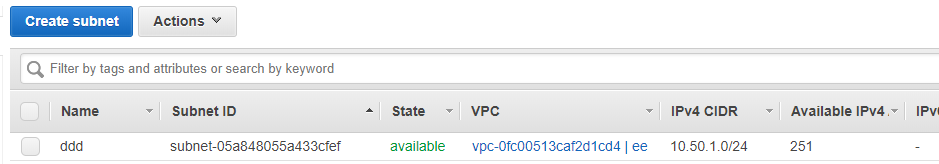
- Fill in the information like VPC name, subnet name and leave the remaining columns as default when the configuration page opens and then select Create VPC option.
- A new dialog box will appear and it shows the work progress. If the work is completed, you can click the OK button.
To select/create an Amazon VPC group
- By using https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/, the Amazon VPC console will be opened.
- Then click the security group option from the navigation bar, then select create a security group option.
- A form will be opened, fill all the information like a name tag, group name, etc in the corresponding boxes. Then select an identifier in the VPC menu for your VPC, then click Yes and create option.
- The list of security group opens and choose the group name and set rules from the list. Next select the Save button.
To launch Instance into Amazon Virtual Private Cloud
- Amazon VPC console is opened by signing into AWS management console
- Choose the same region during the creation of the VPC and security groups.
- From the navigation bar, choose the Launch Instance option.
- A new page will appear, select the AMI which you want.
- You can see the appearance of a new page. Select an Instance Type from the newly opened page and click the hardware configuration. Then choose Next: Configure Instance Details.
- From the Network list, choose the newly created VPC. Then from the Subnet list, choose subnet. Then leave the remaining settings as default and select Next till the Tag Instance page.
- Tag the instance with the Nametag from the Tag Instance page, from the list of multiple instances that will help to search your instance. Then select Next: Configure Security Group.
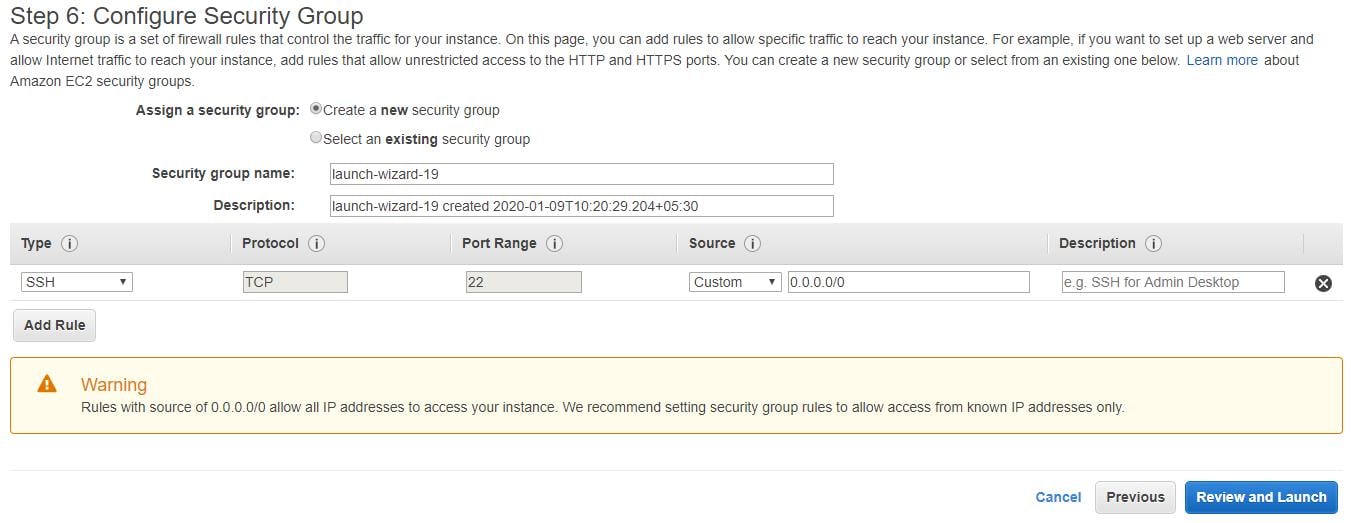
- In the Configure Security Group page, you should choose the newly created group in the list and then, click Review and Launch option.
- From the Review Instance Launch page, you must inspect your instance information, then choose Launch.
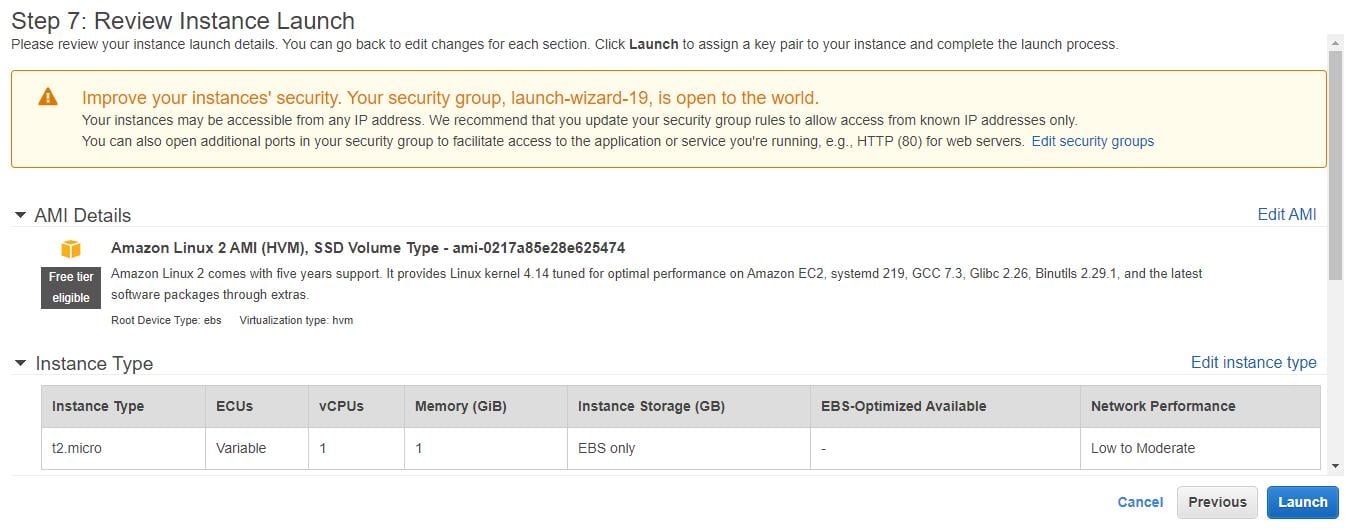
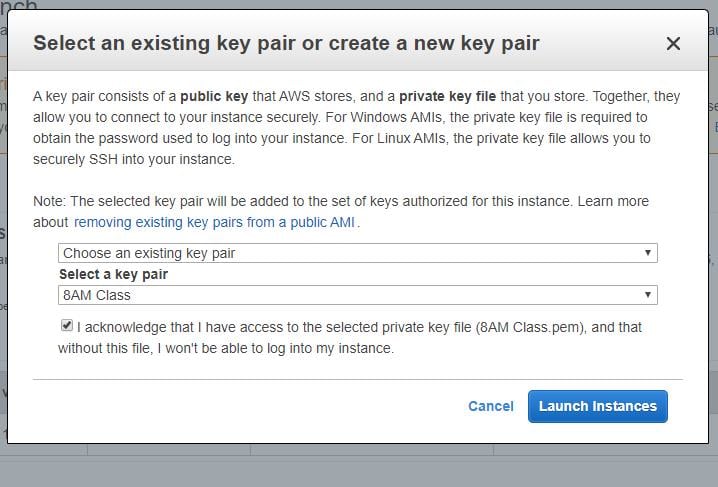
- A new dialog box will open. In that select, the option Select to create a new key pair or an existing key pair and then select the Launch Instances button.
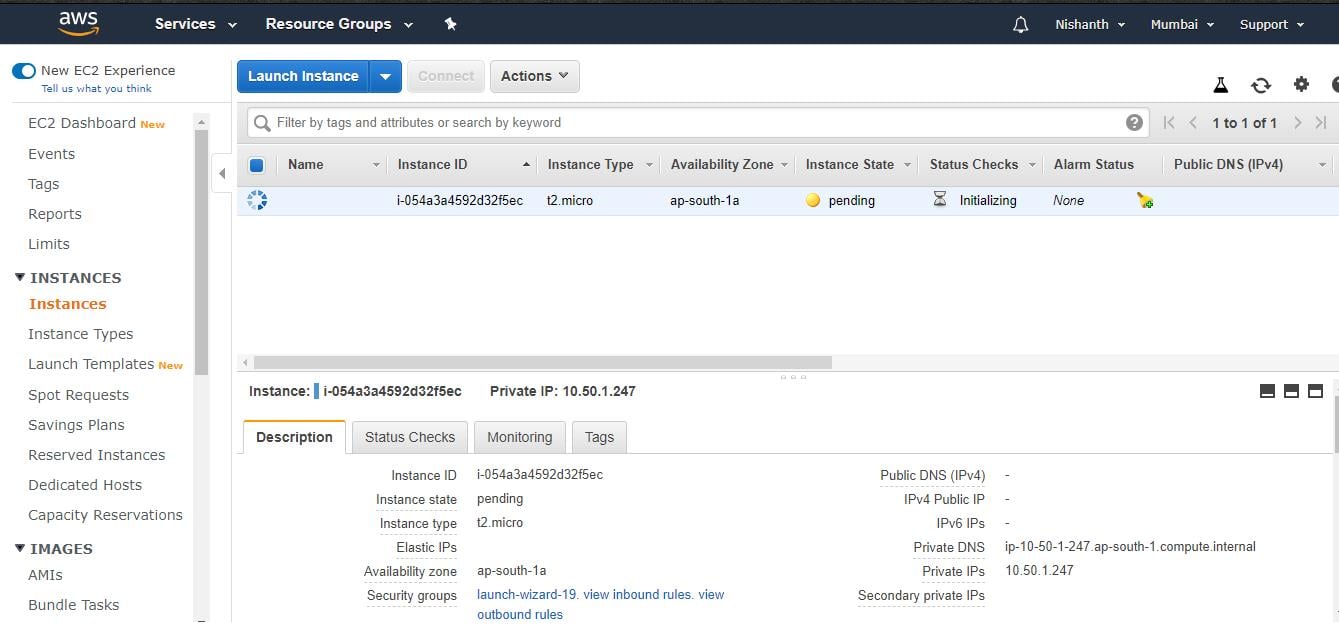
- Finally, the confirmation page will open, which shows every information associated with instances.
Assign Elastic IP Address to VPC Instances
- Amazon VPC console will be opened by clicking the https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/ link.
- Then choose Elastic IP’s option from the navigation bar.
- You have to choose to Allocate New Address. Then click Yes, Allocate option.
- From the list choose your Elastic IP address, then click Actions, and next select the Associate Address option.
- Step 5 − A new dialog box will appear, from the Associate with a list of dialog box choose the Instances. In the Instance list, choose the Instance and finally choose Yes, Associate option.
To delete an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud
You can delete your Amazon VPC at any time. However, you should terminate all instances in the VPC, and delete VPC peering connections first. When you delete an Amazon VPC using the VPC console, it deletes all its components, such as security groups, subnets, route tables, internet gateways, network ACLs, and DHCP options.
Below steps are used to delete Amazon VPC without damaging any resources related to it as follows:
- Amazon VPC console will be opened by clicking the https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/ link.
- Then choose Instances option from the navigation bar.
- From the list, choose Instance. Next, choose the Actions, then select Instance State and then Terminate button.
- A dialog box will appear, in that expand the Release attached Elastic IPs section, and choose the checkbox near Elastic IP address. Select the Yes, Terminate button.
- Again Amazon VPC console will be opened by clicking https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/ link.
- You have to choose the VPC in the navigation bar. Next, choose Actions & finally select, Delete VPC button.
- A final proof message will display on the screen. Click the Yes and then Delete button.
Features of Amazon VPC service
- Numerous connectivity options
Numerous connectivity options available in the Amazon VPC as follows:
- Amazon VPC can be connected with the Internet directly through public subnets.
- Amazon VPC can be connected with the Internet by using Network Address Translation through private subnets.
- You can establish a secure connection to your data center through encrypted IPsec (Internet Protocol sec) hardware (Virtual Private Network) a VPN connection.
- You can create a private connection with other VPCs and can share resources.
- By combining the datacenter and the connection of VPC, there is a way to configure Amazon VPC routing tables to route all traffic flow to its desired destinations.
- Ease to use
Amazon VPC can be created in a simple step by choosing network set-ups with changing needs. Select “Start VPC Wizard”, next Subnets, route tables, security groups, and IP ranges will be created automatically.
- Ease to backup data
By using Amazon EBS volumes, You can backup the data values from the datacenter regularly into Amazon EC2 instances.
- Ease to extend the network by using VPC Cloud
Introduce extra web servers, move applications, and expand storage space by attaching it with VPC.


