
Data Types in Java
Data Types in Java
- Data Types can be defined as the set of values which can be stored in a variable along with the operations that can be perform defined ed on those values.
- Data types are used to identify the type data.
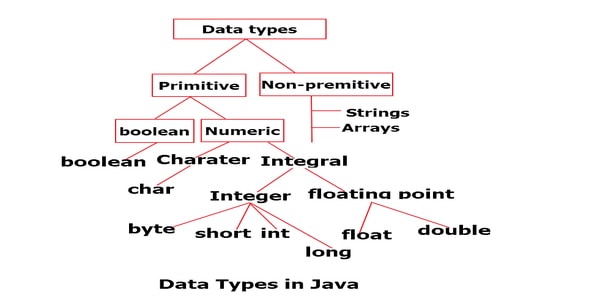
| Primitive Type | Size | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Wrapper Type |
| char | 16-bit | Unicode 0 | Unicode 216-1 | Character |
| byte | 8-bit | -128 | +127 | Byte |
| short | 16-bit | -215 (-32,768) | +215-1 (32,767) | Short |
| Int | 32-bit | -231 (-2,147,438,648) | +231-1 (2,147,483,647) | Integer |
| long | 64-bit | -263 (-9,223,372,036,775,808) | +263-1 (9,223,372,036,854,775,807) | Long |
| Float | 32-bit | Approx range 1.4e-045 to 3.4e+038 | Float | |
| Double | 64-bit | Approx range 4.9e-324 to 1.8e+308 | Double | |
| boolean | 1-bit | true or false | Boolean |
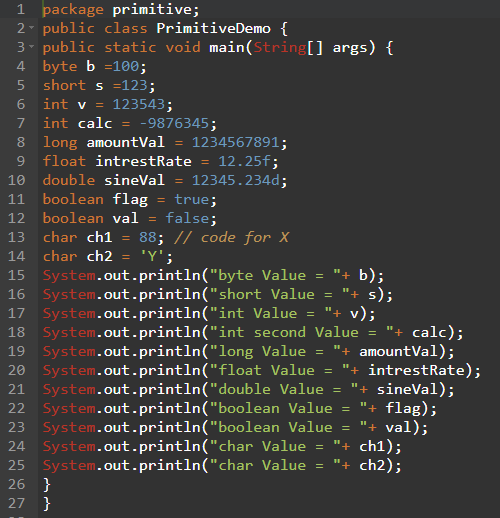
Example program to demonstrate the data types.
Integer Types
Byte
It can store Whole Number from -128 to 127.
Example:
byte myNum = 100; System.out.println(myNum);
Short
It can Store whole number from -32768 to 32767
Example:
short myNum = 5000; System.out.println(myNum);
Int
It can Store whole number -214748648 to 214783647. In general, and in our tutorial, In Our data type is preferred data type when we creat variable with a numeric Value.
Example:
int myNum = 100000; System.out.println(myNum);
Long
It can Store whole numbers -922337203685775808 to 9223372036854775807. This is used when int is not large enough to store the value.
Note: That we should end the value with an ‘L’.
Example:
long myNum = 15000000000L; System.out.println(myNum);
Click Here-> Get Prepared for Java Interviews
Floting Point Types
we should use a floating-type whenever we need a number with a decimal, such as 9.99 or 3.14515
Flot
It can store fractional numbers from 3.4e-038 to 3.4e+038.
Note: That we should end the value with an ‘F’
Example:
float myNum = 5.75f; System.out.println(myNum);
Double
It can store fractional numbers from 1.7e-308to1.7e+038
Note: That we should end the value with a ‘d’:
Example:
double myNum = 19.99d; System.out.println(myNum);
Scientific Numbers
Floating-Point number can be scientific number with ‘e’ to indicate the power of 10:
Example:
float f1 = 35e3f; double d1 = 12E4d; System.out.println(f1); System.out.println(d1);
Booleans
A boolean data type is declared with the Boolean Keywords and can only allow the values of false:
Example:
boolean isJavaFun = true; boolean isFishTasty = false; System.out.println(isJavaFun); // Outputs true System.out.println(isFishTasty); // Outputs false
Boolean Values are mostly used for conditional testing.
Characters
It is used to store a single character. The character must be bounded by single quotes, like ‘A’ or ‘c’:
Example:
char myGrade = 'B'; System.out.println(myGrade);
Alternatively, we can use ASCII value to display certain Characters:
Example:
char a = 15, b = 61 c = 65; System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c);
Strings
It is used to store a sequence of characters(text). String values must be surrounded by double quotes:
Example:
String greeting = "Hello Besant Technologies"; System.out.println(greeting);
A string in Java is really a non-premitive data type, because it refer to an object
Click Here-> Get Java Training with Real-time Projects

