
Java Operators
The operator is a symbol that says the compiler to perform explicit mathematical or logical manipulations.
Types of Operators
- Unary Operators
- Binary Operators
- Ternary Operators
Unary operators
Unary operations have only one operand.
Example:
! & ~ * ++ — + –
Binary operators
The binary operators are operating on two operands. These operators can be arithmetic operators, relational, logical operators, bitwise, assignment operators.
Arithmetic Operators
Example:
+ – * / %
These operators are used in arithmetic expressions.
Example:
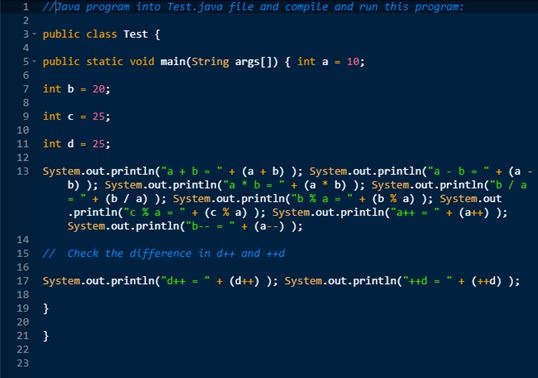
Output:

Relational Operators:
== != > < >= <=
These operators are used in relational operations. The relational operations always give 0 (or False) or 1 (or True).
Example:
Java program in Test.java file and compile and run this program. :
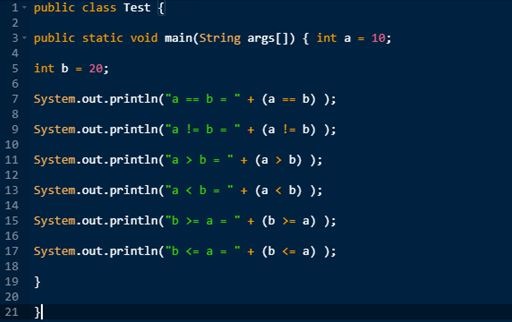
Output:

Logical Operators
The logical operators supported by Java
|| and !
Logical operators are used in logical expressions. Such expressions always give 0 (or False) or 1 (or True).
Example:
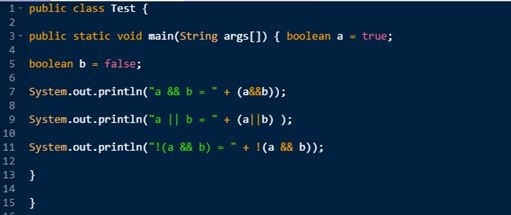
Output:

Click Here-> Get Prepared for Java Interviews
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operator works on bits.
& | ^ ~ << >>
The Bitwise operators supported by C++ are listed in the following below table.
Example:
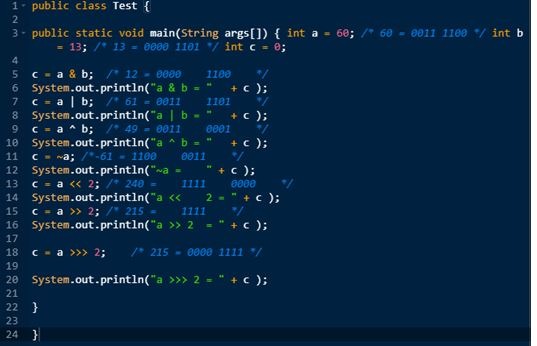
Output:

Shorthand operators
We combine the assignment operators with arithmetic operators and bitwise operators. Such operators are called as shorthand operators.
Example:
+ = -= * = /= %= &= |= ^=
Assignment Operator
It is an operator used to assign a value to a variable.
Syntax:
variable = value or expression;
int a=5;
Special Operators
Some special operators are there in C++.
Example:
sizeof() comma(,) dot(.) pointer(*)
Ternary operators or conditional operators
The ternary operators are those operators that operate on three or more operands. Ternary operator is also called as conditional operator. This operator can be used as an alternative to if-else statement.
Precedence of operators or Hierarchy of operators
If an expression contains multiple operators, the order in which operations are to be carried out is called hierarchy.
Example:
x = 3 + 1 * 5;
Here x is assigned 08, not 20 because operator * has higher precedence than +. First, multiply 1 and 5 and then adds into 3 and assign it to the variable x.
InstanceOf Operator
The instanceOf operator is wriiten as:
( Object reference variable ) instanceOf (class/interface type)
Precedence of Java Operators:
| Category | Operator | Associativity | ||||||
| Postfix | () [] . (dot operator) | Left to right | ||||||
| Unary | ++ – – ! ~ | Right to left | ||||||
| Multiplicative | * / % | Left to right | ||||||
| Additive | + – | Left to right | ||||||
| Shift | >> >>> << | Left to right | ||||||
| Relational | > >= < <= | Left to right | ||||||
| Equality | == != | Left to right | ||||||
| Bitwise AND | & | Left to right |
Click Here-> Get Java Training with Real-time Projects

